
Heat pumps are a type of HVAC system that can both heat and cool a home or building, making them a versatile and energy-efficient option for climate control. At their core, heat pumps rely on the principles of thermodynamics and the transfer of heat energy.
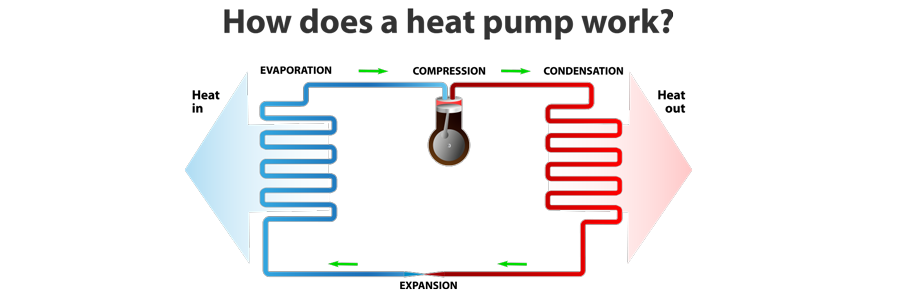
The basic components of a heat pump include an evaporator coil, a compressor, a condenser coil, and a reversing valve. The evaporator coil is located inside the home and absorbs heat from the air or ground, while the condenser coil is located outside the home and releases that heat into the air or ground. The compressor is the device that circulates the refrigerant between these two coils, and the reversing valve switches the direction of the refrigerant flow to allow for heating or cooling.
When the heat pump is set to heat mode, the refrigerant flows through the evaporator coil and absorbs heat from the surrounding air or ground. This heat energy is then compressed by the compressor and transferred to the condenser coil, where it is released into the air or ground outside. The reversing valve allows the refrigerant to flow in this direction, creating a cycle that can continue to extract heat from the air or ground even when temperatures are low.
When the heat pump is set to cool mode, the process is reversed. The refrigerant flows in the opposite direction, absorbing heat from inside the home and releasing it outside. The reversing valve is used to change the direction of the refrigerant flow as needed.
Heat pumps are particularly efficient because they do not generate heat directly, but rather transfer it from one location to another. This means that they can provide a lot of heating or cooling power for relatively little energy input. Additionally, many heat pumps are designed to work in tandem with other energy-efficient systems, such as geothermal heat exchangers or solar panels, to further reduce energy usage and costs.
In summary, heat pumps work by using refrigerant to transfer heat energy between the inside and outside of a home or building. They rely on the principles of thermodynamics and the transfer of heat energy, making them an efficient and environmentally-friendly option for climate control.

You must be logged in to post a comment.